Table Of Content

King created protein subunits that arrange themselves into a virus-like particles (VLPs), displaying viral antigens in regular arrays to elicit an effective immune reaction. Synthetic VLPs offer more opportunities for customization than natural ones, opening up the possibility of vaccines for intractable viruses such as RSV and HIV. King and his colleagues fused the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein to self-assembling nanoparticles and are working on creating the optimal antigen display for a coronavirus vaccine. Silva studied the 3D structure of IL-2 in its high-affinity conformation, the shape it assumes when bound to all three receptor subunits. He built a new protein that emulated that shape but was “otherwise unrelated in topology or amino acid sequence.” It also lacked any binding site for the alpha receptor subunit. By constructing a completely novel protein instead, the team could create a highly stable molecule that bound with high efficiency to the beta and gamma subunits and ignored the alpha subunit.

Ben FryGraduate Student
Now, our group has developed a computational method called COMBS that can generate protein sequences from scratch that are able to tightly and specifically bind to challenging targets. COMBS thus enables the rapid generation of proteins that may act as sensors, therapeutics, or delivery vehicles. Aminoacyl tRNA synthetases link amino acids with their cognate tRNAs and are thus critical players in the expansion of the genetic code. However, it has proven incredibly difficult to engineer synthetases to recognize polar, non-natural amino acids that mimic common post-translational modifications (PTMs) of proteins. The ability to precisely program PTMs and monitor their effects on cell fate in disease-relevant mammalian cells has been a longstanding goal.
Roksana Azad, PhDPostdoctoral Research Fellow
We have lots of exciting projects involving protein design, high-throughput experiments, and structure determination. Roksana grew up in Bangladesh and later immigrated to the United States, where she completed her B.S. She received her Ph.D. in Biochemistry and Molecular Biophysics from the CUNY Advanced Science Research Center working in Prof. Kevin Gardner's lab. During her Ph.D., Roksana studied the superfamily of PAS/LOV sensory domains and their regulatory control of Ser/Thr kinases in plants and humans. Her thesis research characterized the structure and function of the allosteric regulation of PAS to control the kinase function using integrated techniques including NMR (high-pressure, 2D/3D), HDX-MS, cryo-EM, and X-ray. In her free time, Roksana is passionate about volunteering in STEM outreach, and she enjoys cooking, watching soccer and cricket, outdoor activities, and keeping up with recent scientific discoveries.
Protein Design Labs, Inc. Becomes PDL BioPharma, Inc.
The Era of Machine Learning for Protein Design, Summarized in Four Key Methods - Towards Data Science
The Era of Machine Learning for Protein Design, Summarized in Four Key Methods.
Posted: Thu, 04 May 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Additionally, the IBRL helps startups understand the best raw materials — sugars, amino acids, etc. — to use in their fermentation process, Jacobson said. Many alt-protein startups mistakenly purchase American Chemical Society (ACS) reagent-grade ingredients, considered the highest standard in terms of ingredient quality, when cheaper options are available to them, he added. IBRL helps "companies go from ... two PhDs in a lab" to creating the processes and technical know-how to create alt proteins at a larger scale. Other institutions, like the University of California, Davis Integrative Center for Alternative Meat and Protein offer similar support to alt-protein startups.
The original concept Baker and colleagues had in mind was to develop algorithms to predict a protein’s final 3D structure. Rosetta simulates the interplay of hydrogen bonds and side chain attractions and repulsions through which a linear chain of amino acids collapses into a thermodynamically favorable state. In the early 2000s, in work spearheaded by then-postdoc Brian Kuhlman (now at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill), Baker’s team figured out how to use Rosetta ‘backward’.
Students and Postdocs
The precise order of amino acids in a protein chain, like the letters in a word, is crucial. The unique functions of a protein stem from its three-dimensional structure, which is determined by the sequence of amino acids composing the protein. Franzi grew up in Germany and graduated from Albert Ludwigs University Freiburg with a BSc in Molecular Medicine and afterwards a MSc in Biochemistry from University of Leipzig. She pursued her PhD at the Max Planck Institute for Terrestrial Microbiology where she worked with Dr. Georg Hochberg in the area of Evolutionary Biochemistry. In her work she investigated self-assembly of proteins and the evolution of biological complexity.
Baker Lab
PDL BioPharma, Inc. is a biopharmaceutical company focused on discovering, developing and commercializing innovative therapies for severe or life threatening illnesses. The beauty of the LOCKR system is that it’s modular and customizable, so rather than going back to the drawing board for each new cellular application, it’s possible to swap out the active domain with different functional elements. ” The pair discussed the idea of enclosing a degron, a protein sequence that helps regulate protein degradation.
Simplifying nanoscale design with regular protein building blocks
This press release contains forward-looking statements involving risks and uncertainties, including statements regarding growth and cash flow, and PDL's actual results may differ materially from those in the forward- looking statements. As we continue to unlock the secrets of proteins and learn to harness their potential, the possibilities for protein design are virtually limitless. In this post, we will delve into the basics of protein design, explore its real-world applications, and learn about the interdisciplinary nature of this fascinating field. The synthetic cytokine neoleukin-2/15 was created in an attempt to jettison some very heavy baggage that has dogged cancer researchers for decades. Since the 1980s, the cytokine interleukin (IL)-2 has tantalized oncologists with the promise of harnessing the immune system to attack tumors. IL-2 naturally stimulates T cell proliferation, but it also exerts ferocious side effects on the body, particularly in the lungs.
Access options
The world of proteins is incredibly complex, offering endless possibilities for exploration and discovery. They are found inside every living thing and act as structural components, transporters, signaling molecules, and much more. Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily. Foldit players have helped make published discoveries through their unique creativity and ingenuity. Research on it began here as an undergraduate project and would go on to form the basis of a spinout company. Algorithm DevelopmentBiomolecular modeling and computational design are at the heart of everything we do.
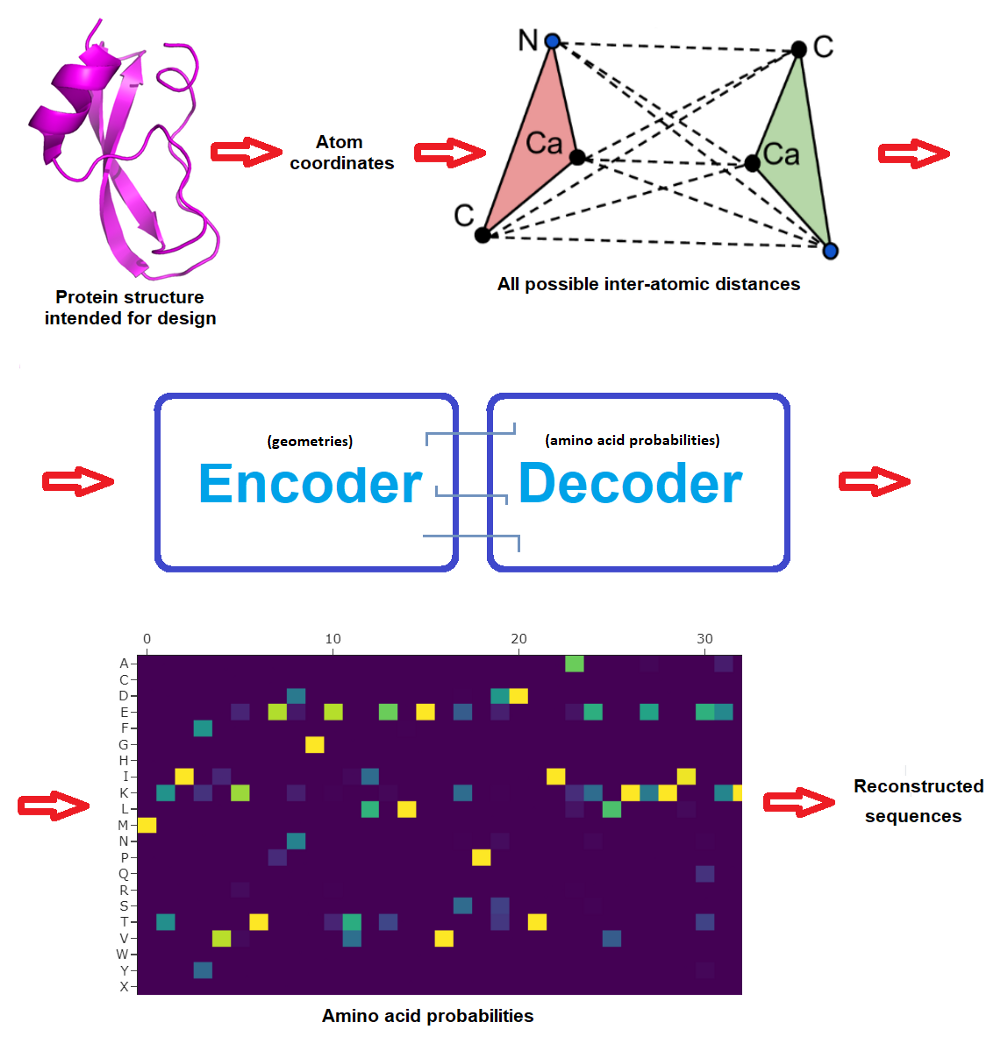
We believe that Artificial Intelligence is starting a revolution in this field, and it will radically change it forever. The exquisite functions of naturally occurring proteins solve the challenges faced during evolution. However, we face challenges today that were not faced during natural evolution. The goal of the Institute for Protein Design (IPD) is to develop and apply methods for designing a whole new world of synthetic proteins to address these challenges.
As an intern with the Rosetta Commons, he worked in Dr. Daniel Kulp’s lab at The Wistar Institute to develop a computational protocol that targets viral glycoprotein epitopes for immune recognition. He is broadly interested in developing new computational techniques for protein design with the hope that they can be used to create the next generation of protein-based therapeutics. Outside of the lab, Ben enjoys exploring the city, hiking, cooking, and playing guitar. To create the algorithm, the scientists trained an AI model with information from hundreds of thousands of known interactions between chemical molecules and the corresponding three-dimensional protein structures.
In addition to predicting protein structures, computational methods also allow scientists to simulate how proteins will interact with other molecules. This information is vital in refining protein designs to optimize their stability, binding affinity, or catalytic activity. Now, without human intervention, a generative AI is able to develop drug molecules from scratch that match a protein structure. This groundbreaking new process ensures right from the start that the molecules can be chemically synthesised.
Meanwhile, insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, helps regulate blood sugar levels by signaling cells to take in glucose from the bloodstream. Raphael's model for evaluating protein structures is posted on bioRxiv as a preprint. The protein system is called LOCKR, for “Latching, Orthogonal Cage/Key Proteins,” and it consists of a six-helix protein that folds into a stable, cage-like formation. The cage can interact with either its own ‘latch’ helix domain, which holds the cage closed, or to another protein—the ‘key’—which triggers a conformational change.

No comments:
Post a Comment